Spam is an unfortunate by-product of having an email address. Spam may seem more annoying than dangerous, but it is wise to treat spam with caution. As email filters become more stringent, spam also becomes more inventive. Many spam emails are tied to phishing attempts, which just means that the email tries to get sensitive information out of you.
In this article, we will go over:
- What is Email Spoofing?
- Types of Phishing
- How to Identify Spam
- Steps Towards Protection
What is Email Spoofing?
Email spoofing refers to when a hacker tries to disguise a malicious email as one from a legitimate source. The scammer can spoof an email a variety of ways. Some popular ways are:
- Creating an email address that is almost identical to a legitimate address
- Forging the From address to look like a legitimate sender
- Forging the display name, but does not change the From address
Spoofing may not seem problematic initially. However, hackers may use the spoofed emails as a way to trick you into sharing sensitive information. When paired with "phishing" schemes or social engineering, spoofed emails can become a real problem, especially for those who aren't on the lookout for them.
Types of Phishing
There are a variety of phishing tactics that can be used to lure people to divulge personal information, some of which we will cover below.
Phishing Links
One common method is to use phishing links. The spoofed message will create a reason for the recipient to visit the link in the email, such as, "You need to update your information for payment to go through." Then they will supply a link that will take the recipient to a website that looks legitimate, but is actually designed to take your information and funnel it back to the hacker.
To someone who has just been told that they need to "update their information" or "input an updated routing number," it can be easy to overlook small inconsistencies in their effort to rectify whatever problem the phishing email has told them they have.
Fake Attachments
Hackers may also use fake attachments to get around stricter email filters. These fake attachments can contain a phishing link to a faked website, though some may also contain ransomware.
Ransomware is a software that takes away your access to your computer until you pay a sum of money to the hacker. When hidden in a fake attachment, the ransomware lies dormant until the recipient tries to open the attachment. When the attachment is opened however, the ransomware will begin to download to the computer. Once downloaded, the ransomware could take the computer hostage, essentially locking out the user until they pay the hacker for its release. You can read more about ransomware in our Ransomware article.
Spearphishing
Spearphishing can be particularly dangerous and hard to detect. The name refers to a targeted attack; (a spear, if you will) that uses information about the recipient against them. The hacker will gather research about the recipient or organization (whether through research or by hacking), then create a message tailored to the recipient. It could be spoofed to appear like it comes from a coworker or boss, or may reference an ongoing project.
While this type of social-engineering phishing is not as common as the other two versions, spearphishing can be much more dangerous. Because it's designed to get the recipient to drop their guard, it can be hard to detect.
How to Identify Spam
However, all is not lost. Here are some ways to help pick spam out from the legitimate emails.
- Check for typos or strange phrasing. This can be indicative of a spam email.
- Check for strange or unfamiliar links. Do not click on strange links
- Check for context. Did your boss or colleague say that they would be sharing an attachment or link with you? If you're getting a bad feeling about the email, get in touch with them (though we recommend using an alternate communication method. Don't reply to the shady email!)
- Be wary of emails asking for personal information. A legitimate business or government organization (like the IRS) will not ask for information like credit card numbers, social security numbers, or passwords over email.
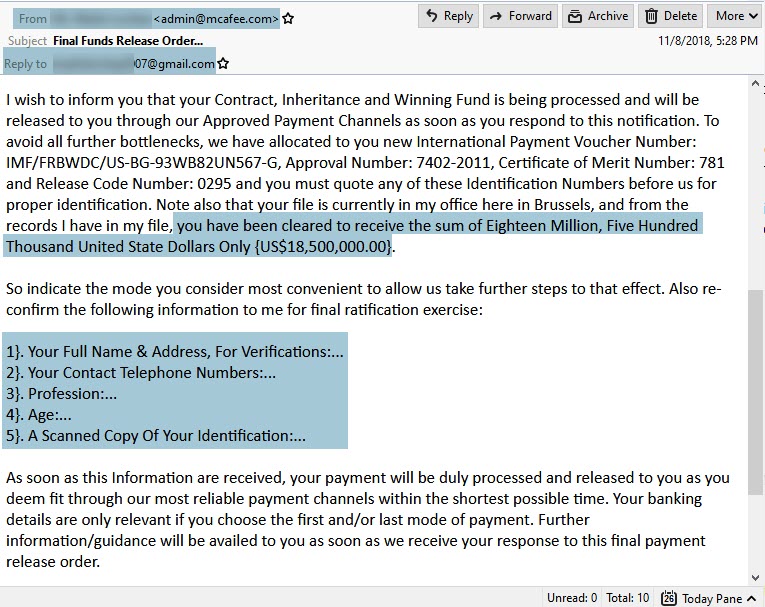
This spam message claims that the recipient is receiving $18 million - they only need to send them some personal information. Notice that the sender spoofed an "[email protected]" address to seem more legitimate. The reply-to email is a different gmail account. - Check to make sure the From and Reply To address match. If they don't, it may be cause for suspicion.
- Does it sound too good to be true? It probably is. A common tactic for hackers is to say that you won money, then ask for your bank information to deposit your "winnings.
If you are suspicious of the message, you can try searching the contents or defining features of the email. For example, look at this spam message. 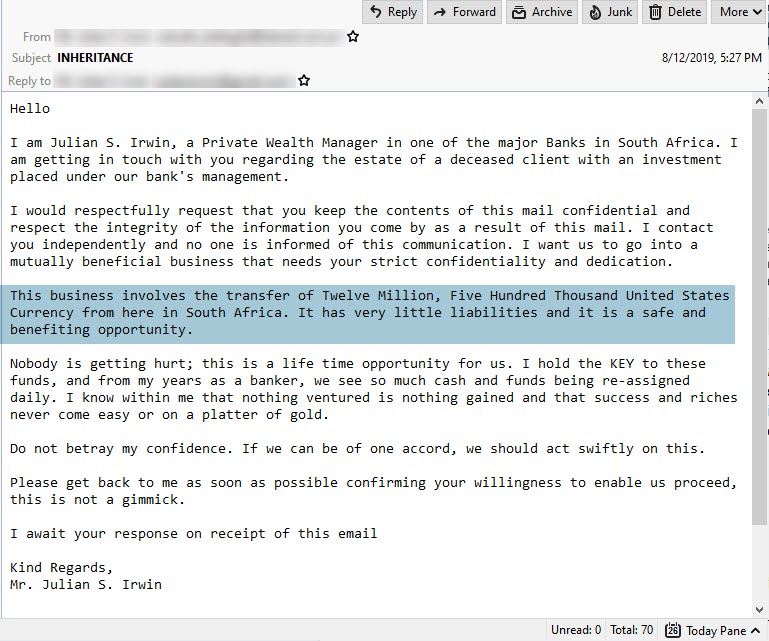
It promises money (and seems shady, overall). So we googled the name of the sender and the email subject. The results show that it is not only spam, but a popular gimmick that's been used for several years. 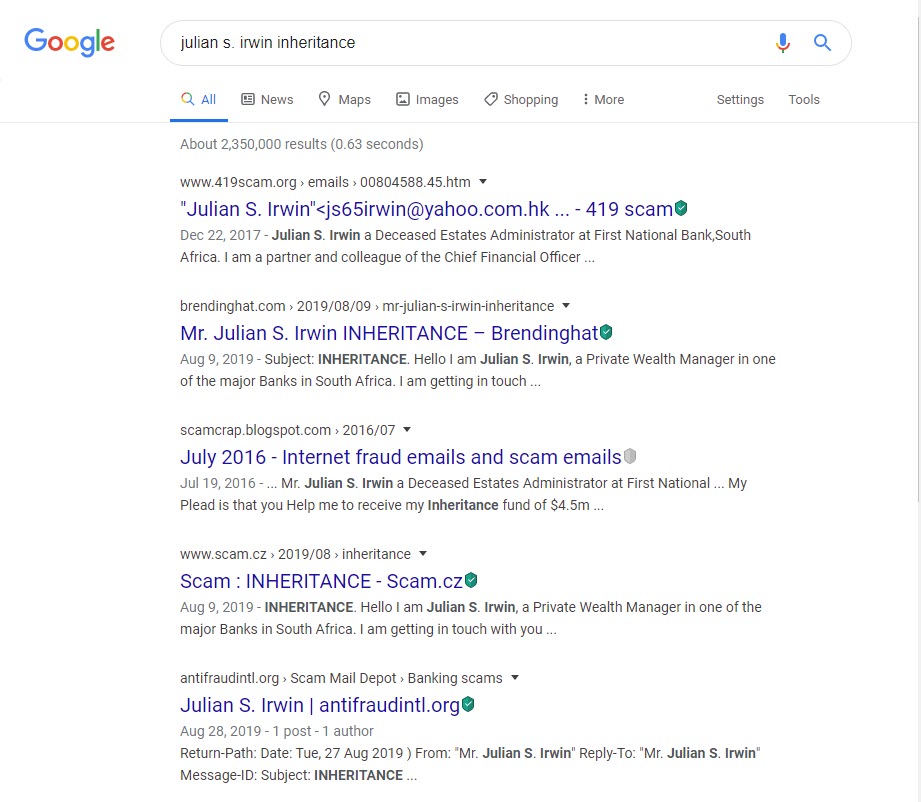
How to Protect Yourself
The best way to protect yourself is to be vigilant and keep up-to-date with current email spam trends.
While our email security filters are being updated all the time, hackers are continuously coming up with new ways to get around them. So just because it made it to your inbox doesn't mean it's safe. We recommend exercising a combination of good email security practices and good judgment.
Pair mailboxes come configured with an array of security filters and protections in place. However, if you want to add more layers of protection, you can check out these tutorials:
- What is an SPF Record? and Adding an SPF Record: Learn about SPF records and how you can put them to work for your email.
- Blacklisting Email Addresses: If you have encountered spam from an address, you can blacklist it so that it can no longer send you emails.
- Junk Emails Are Being Send From My Address: If spammers are spoofing your email to send others spam, check out this article to see how you can potentially stop it.
- Junk Email Filtering Overview: Learn about your junk mail filtering options that can be customized in the ACC.
